Deque 란?
덱(deque)은 양쪽 끝에서 삽입과 삭제가 모두 가능한 자교 구조의 한 형태이다.
두 개의 포인터를 사용하여 양쪽에서 삭제와 삽입을 발생시킬 수 있다. 큐와 스택을 합친 형태로 생각할 수 있다.
by. wikipedia
즉 Deque란 양쪽 끝에서 삽입/삭제가 가능하며, 큐와 스택을 합친 자료구조이다.
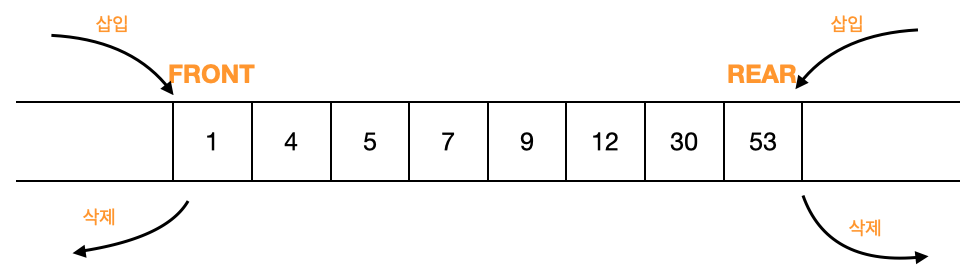
- 요소를 양쪽에서 삽입/삭제 가능해야 함.
- 위 삽입 / 삭제 행위의 시간 복잡도가 O(1) 이어야 함.
Deque 구현
시간복잡도를 지키면서 양쪽에서 삽입/삭제 가능한 형태의 자료구조는 단일 연결 리스트를 생각할 수 있다.
각 노드들이 연결된 노드들과 값을 저장할 Node 클래스를 생성한다.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
Deque는 다음과 같은 속성을 가진다.
- length : 연결된 노드들의 길이
- frontNode : 제일 앞의 노드
- rearNode : 제일 마지막의 노드
그리고 다음과 같은 기본적인 매서드를 제공한다.
- unshift(value) : 덱의 앞에서 노드 삽입
- shift() : 덱의 앞에서 노드 삭제
- front() : 덱의 제일 앞의 노드 조회
- push(value) : 덱의 뒤에서 노드 삽입
- pop() : 덱의 뒤에서 노드 삭제
- last() : 덱의 제일 마지막 노드 조회
- at(value) : 특정 인덱스 조회
- toArray() : 덱을 배열로 변환
추가적으로 spread 연산자 및 인덱스 접근, map 매서드를 지원한다.
덱 클래스 정의
class Deque {
constructor() {
this.init();
}
init() {
this.length = 0;
this.frontNode = null;
this.rearNode = null;
}
}
덱의 양쪽에서 노드 조회
front() {
return this.frontNode ? this.frontNode.value : undefined;
}
last() {
return this.rearNode ? this.rearNode.value : undefined;
}
덱의 앞에서 노드 삽입/삭제
unshift(value) {
const node = new Node(value);
if(!this.frontNode) {
this.frontNode = node;
this.rearNode = node;
} else {
const prevFront = this.frontNode;
prevFront.prev = node;
node.next = prevFront;
this.frontNode = node;
}
this.length += 1;
return this.length;
}
shift() {
if(this.length === 0) return null;
const value = this.frontNode.value;
if(this.length === 1) this.init();
else {
this.frontNode = this.frontNode.next;
this.frontNode.prev = null;
this.length -= 1;
}
return value;
}
덱의 뒤에서 노드 삽입/삭제
push(value) {
const node = new Node(value);
if(this.length === 0){
this.frontNode = node;
this.rearNode = node;
} else {
const prevRear = this.rearNode;
prevRear.next = node;
node.prev = prevRear;
this.rearNode = node;
}
this.length += 1;
return this.length;
}
pop() {
if(this.length === 0) return;
const value = this.rearNode.value;
if(this.length === 1) this.init();
else {
this.rearNode = this.rearNode.prev;
this.rearNode.next = null;
this.length -= 1;
}
return value;
}
특정 인덱스 조회
at(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.length) return undefined;
let node = this.frontNode;
for(let i=0; i<index; i++) node = node.next;
return node.value;
}
덱을 배열로 변환
toArray() {
const length = this.length;
const array = [];
let node = this.frontNode;
for(let i=0; i<length; i++) {
array.push(node.value);
node = node.next;
}
return array;
}
Spread 연산자 지원
Spread 연산자를 지원하기 위해서는 Deque 클래스가 iterable 해야한다.
Symbol.iterator 매서드를 구현하고 yield 키워드를 통하여 값을 반환한다.
*[Symbol.iterator]() {
let node = this.frontNode;
while(node) {
yield node.value;
node = node.next;
}
}
인덱스 접근 지원
array의 장점 중 하나가 인덱스 접근으로 인한 직관적인 표기법이라고 생각한다.
그래서 Deque에서도 deque[1]과 같이 접근할 수 있도록 인덱스 접근을 지원해주기로 했다.
class Deque {
constructor() {
// init 코드
return new Proxy(this, {
get: (target, prop) => {
if(typeof prop === "string" && !isNaN(prop)) {
const index = parseInt(prop);
const node = target.atProxy(index);
return node ? node.value : undefined;
}
return target[prop];
},
set: (target, prop, value) => {
if(typeof prop === "string" && !isNaN(prop)) {
const index = parseInt(prop);
const node = target.atProxy(index);
if(node) { node.value = value; return true; }
return false;
}
target[prop] = value;
return true;
}
});
}
atProxy(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.length) return undefined;
let node = this.frontNode;
for(let i=0; i<index; i++) node = node.next;
return node;
}
/*
... 이전 코드
*/
}
forEach, map 매서드 지원
array에서 자주 사용하는 forEach, map 매서드도 지원해주기로 했다.
forEach(callback) {
let node = this.frontNode;
let index = 0;
while(node) {
callback(node.value, index, this);
node = node.next;
index++;
}
}
map(callback) {
const result = [];
let node = this.frontNode;
let index = 0;
while(node) {
result.push(callback(node.value, index, this));
node = node.next;
index++;
}
return result;
}
전체 코드
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class Deque {
constructor() {
this.init();
return new Proxy(this, {
get: (target, prop) => {
if(typeof prop === "string" && !isNaN(prop)) {
const index = parseInt(prop);
const node = target.atProxy(index);
return node ? node.value : undefined;
}
return target[prop];
},
set: (target, prop, value) => {
if(typeof prop === "string" && !isNaN(prop)) {
const index = parseInt(prop);
const node = target.atProxy(index);
if(node) { node.value = value; return true; }
return false;
}
target[prop] = value;
return true;
}
});
}
init() {
this.length = 0;
this.frontNode = null;
this.rearNode = null;
}
at(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.length) return undefined;
let node = this.frontNode;
for(let i=0; i<index; i++) node = node.next;
return node.value;
}
front() {
return this.frontNode ? this.frontNode.value : undefined;
}
last() {
return this.rearNode ? this.rearNode.value : undefined;
}
unshift(value) {
const node = new Node(value);
if(!this.frontNode) {
this.frontNode = node;
this.rearNode = node;
} else {
const prevFront = this.frontNode;
prevFront.prev = node;
node.next = prevFront;
this.frontNode = node;
}
this.length += 1;
return this.length;
}
shift() {
if(this.length === 0) return null;
const value = this.frontNode.value;
if(this.length === 1) this.init();
else {
this.frontNode = this.frontNode.next;
this.frontNode.prev = null;
this.length -= 1;
}
return value;
}
push(value) {
const node = new Node(value);
if(this.length === 0){
this.frontNode = node;
this.rearNode = node;
} else {
const prevRear = this.rearNode;
prevRear.next = node;
node.prev = prevRear;
this.rearNode = node;
}
this.length += 1;
return this.length;
}
pop() {
if(this.length === 0) return;
const value = this.rearNode.value;
if(this.length === 1) this.init();
else {
this.rearNode = this.rearNode.prev;
this.rearNode.next = null;
this.length -= 1;
}
return value;
}
toArray() {
const length = this.length;
const array = [];
let node = this.frontNode;
for(let i=0; i<length; i++) {
array.push(node.value);
node = node.next;
}
return array;
}
*[Symbol.iterator]() {
let node = this.frontNode;
while(node) {
yield node.value;
node = node.next;
}
}
forEach(callback) {
let node = this.frontNode;
let index = 0;
while(node) {
callback(node.value, index, this);
node = node.next;
index++;
}
}
map(callback) {
const result = [];
let node = this.frontNode;
let index = 0;
while(node) {
result.push(callback(node.value, index, this));
node = node.next;
index++;
}
return result;
}
atProxy(index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.length) return undefined;
let node = this.frontNode;
for(let i=0; i<index; i++) node = node.next;
return node;
}
}
마무리
자바스크립트로 알고리즘 문제를 풀면서 매번 shift나 unshift를 사용하는 문제를 마주치면 최대한 사용하지 않고 풀 수 있도록 회피했다.
하지만.. 이번에 회피할 수 없고 deque를 구현하지 않으면 시간초과가 나는 문제를 마주했다.ㅠㅠ
그래서 Deque의 필수 매서드들과 장점이라고 생각하는 spread 연산자 및 인덱스 접근을 지원하는 Deque를 구현해보았다!
다음에는 Priority Queue를 구현해봐야겠다!
'💾 Algorithm > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JS] Map 살펴보기 (0) | 2025.01.02 |
|---|---|
| [C++] map Class 활용법 (0) | 2023.05.26 |
| [C++] multiset Class 활용법 (2) | 2023.05.25 |
